How Nubank refactors millions of lines of code to improve engineering efficiency with Devin
Overview
One of Nubank’s most critical, company-wide projects for 2023-2024 was a migration of their core ETL — an 8 year old, multi-million lines of code monolith — to sub-modules. To handle such a large refactor, their only option was a multi-year effort that distributed repetitive refactoring work across over one thousand of their engineers. With Devin, however, this changed: engineers were able to delegate Devin to handle their migrations and achieve a 12x efficiency improvement in terms of engineering hours saved, and over 20x cost savings. Among others, Data, Collections, and Risk business units verified and completed their migrations in weeks instead of months or years.
The Problem
Nubank was born into the tradition of centralized ETL FinServ architectures. To date, the monolith architecture had worked well for Nubank — it enabled the developer autonomy and flexibility that carried them through their hypergrowth phases. After 8 years, however, Nubank’s sheer volume of customer growth, as well as geographic and product expansion beyond their original credit card business, led to an entangled, behemoth ETL with countless cross-dependencies and no clear path to continuing to scale.
For Nubankers, business critical data transformations started taking increasingly long to run, with chains of dependencies as deep as 70 and insufficient formal agreements on who was responsible for maintaining what. As the company continued to grow, it became clear that the ETL would be a primary bottleneck to scale.
Nubank concluded that there was an urgent need to split up their monolithic ETL repository, amassing over 6 million lines of code, into smaller, more flexible sub-modules.
Nubank’s code migration was filled with the monotonous, repetitive work that engineers dread. Moving each data class implementation from one architecture to another while tracing imports correctly, performing multiple delicate refactoring steps, and accounting for any number of edge cases was highly tedious, even to do just once or twice. At Nubank’s scale, however, the total migration scope involved more than 1,000 engineers moving ~100,000 data class implementations over an expected timeline of 18 months.
In a world where engineering resources are scarce, such large-scale migrations and modernizations become massively expensive, time-consuming projects that distract from any engineering team’s core mission: building better products for customers. Unfortunately, this is the reality for many of the world’s largest organizations.
The Decision: an army of Devins to tackle subtasks in parallel
At project outset in 2023, Nubank had no choice but to rely on their engineers to perform code changes manually. Migrating one data class was a highly discretionary task, with multiple variations, edge cases, and ad hoc decision-making — far too complex to be scriptable, but high-volume enough to be a significant manual effort.
Within weeks of Devin’s launch, Nubank identified a clear opportunity to accelerate their refactor at a fraction of the engineering hours. Migration or large refactoring tasks are often fantastic projects for Devin: after investing a small, fixed cost to teach Devin how to approach sub-tasks, Devin can go and complete the migration autonomously. A human is kept in the loop just to manage the project and approve Devin’s changes.
The Solution: Custom ETL Migration Devin
A task of this magnitude, with the vast number of variations that it had, was a ripe opportunity for fine-tuning. The Nubank team helped to collect examples of previous migrations their engineers had done manually, some of which were fed to Devin for fine-tuning. The rest were used to create a benchmark evaluation set. Against this evaluation set, we observed a doubling of Devin’s task completion scores after fine-tuning, as well as a 4x improvement in task speed. Roughly 40 minutes per sub-task dropped to 10, which made the whole migration start to look much cheaper and less time-consuming, allowing the company to devote more energy to new business and new value creation instead.
Devin contributed to its own speed improvements by building itself classical tools and scripts it would later use on the most common, mechanical components of the migration. For instance, detecting the country extension of a data class (either ‘br’, ‘co’, or ‘mx’) based on its file path was a few-step process for each sub-task. Devin’s script automatically turned this into a single step executable — improvements from which added up immensely across all tens of thousands of sub-tasks.
There is also a compounding advantage on Devin’s learning. In the first weeks, it was common to see outstanding errors to fix, or small things Devin wasn’t sure how to solve. But as Devin saw more examples and gained familiarity with the task, it started to avoid rabbit holes more often and find faster solutions to previously-seen errors and edge cases. Much like a human engineer, we observed obvious speed and reliability improvements with every day Devin worked on the migration.
“Devin provided an easy way to reduce the number of engineering hours for the migration, in a way that was more stable and less prone to human error. Rather than engineers having to work across several files and complete an entire migration task 100%, they could just review Devin’s changes, make minor adjustments, then merge their PR”
Jose Carlos Castro, Senior Product Manager
Use cases
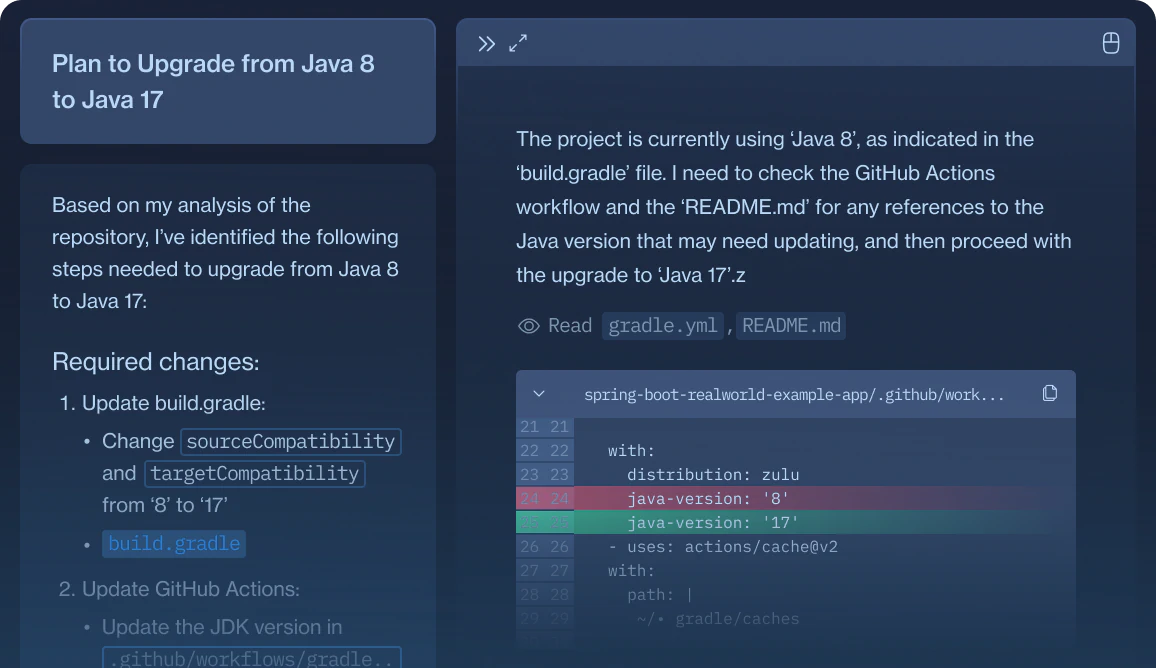
Java Version Upgrades
Automate Java 8 → 17 migrations across enterprise applications.
.NET Upgrades
Upgrade enterprise applications from legacy .NET versions to .NET 8.
Security Remediation
Auto-fix SAST-detected vulnerabilities and code issues from SonarQube, Veracode, and others.
Mainframe / COBOL Migrations
Migrate decades-old COBOL systems into modern, cloud-native services.
Legacy ETL Migrations
Break monolithic ETL pipelines into scalable, event-driven microservices.
Custom & Proprietary Systems
Migrate and maintain proprietary or custom systems unsupported by off-the-shelf tools.
Customer stories

Press release
Goldman Sachs is piloting its first autonomous coder, Devin.

Press release
Citi rolls out Devin to 40,000 developers for autonomous code, testing, and documentation.

Case study
Nubank refactors millions of lines of code with Devin to boost engineering efficiency.

Case study
Ramp eliminates tens of thousands of hours of technical debt with Devin, freeing engineers to build new products.

Case study
Bilt uses Devin to help engineers overcome coder’s block and accelerate complex projects.
Enterprise Security & Functionality
Contact our sales team Contact
our sales team
Contact us Java Version Upgrades
Java Version Upgrades
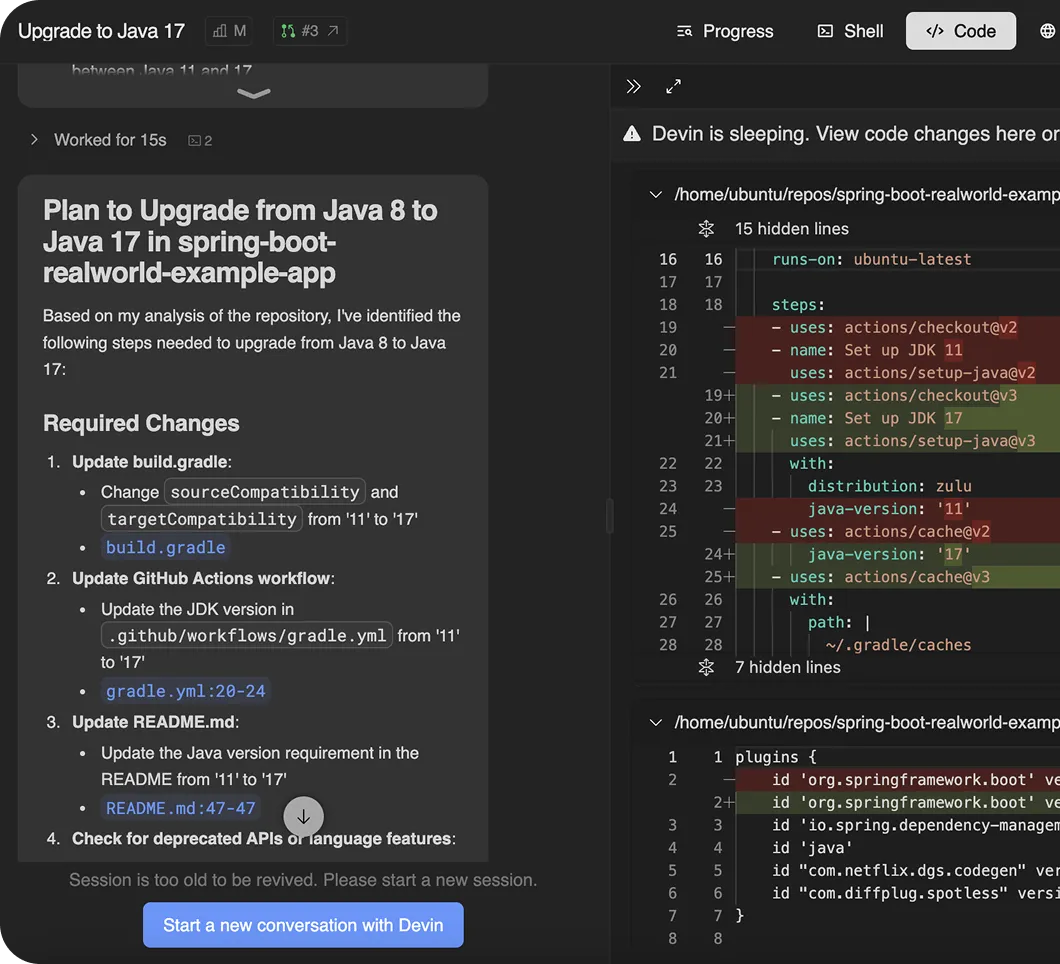
Devin automates upgrades to Java 17 by updating build files, modernizing libraries (e.g., Joda-Time → java.time), and handling custom dependencies from your artifact store. It spans the full SDLC, including CI/CD modernization, and ensures validated outputs through incremental migration with regression tests.

Devin’s Workflow<br/>Java 8 → 17
- Analyze & plan Identify Java 8 dependencies and build files.
- Scaffold project Update Gradle/Maven configs and CI workflows.
- Migrate logic Replace deprecated APIs, upgrade libraries, and integrate with internal artifact mirrors.
- Test parity Run regression tests to confirm successful incremental migration.
- Open PR Open pull request with code and migration notes.

Devin Prompt
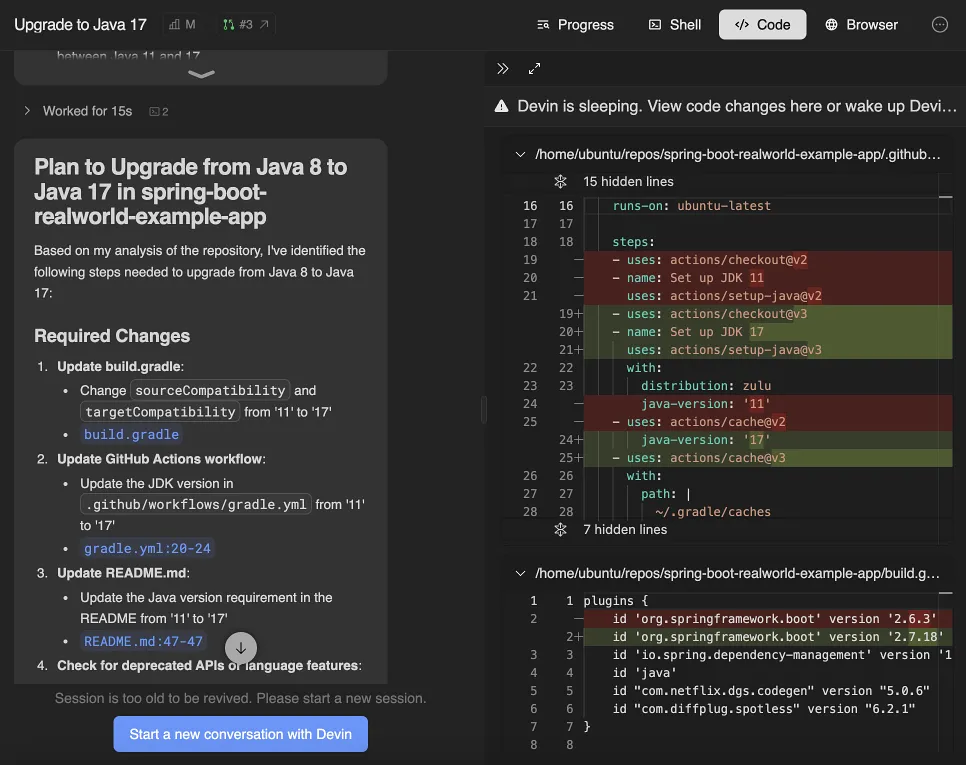
Hey Devin,
Please upgrade the BankOfDevin/BankingServer repository from Java 8 to Java 17. Here’s your task breakdown:
Required Changes
Update build.gradle
- Change
sourceCompatibilityandtargetCompatibilityfrom ‘8’ to ‘17’
<ref_file file="/home/ubuntu/repos/BankOfDevin/BankingServer/build.gradle" />Update GitHub Actions workflow
- Update the JDK version in
.github/workflows/gradle.ymlfrom ‘8’ to ‘17’
<ref_snippet file="/home/ubuntu/repos/BankOfDevin/BankingServer/.github/workflows/gradle.yml" lines="20-24" />Update README.md
- Update the Java version requirement in the README from ‘8’ to ‘17’
<ref_snippet file="/home/ubuntu/repos/BankOfDevin/BankingServer/README.md" lines="47-47" />Check for deprecated APIs or language features
- Review the codebase for features removed or changed since Java 8
- Pay attention to:
- Internal JDK APIs removed in Java 17
- Deprecated methods no longer available
- Reflection and security model changes
Test the application
- Run the full test suite to confirm compatibility with Java 17
- Perform manual testing to verify runtime behavior
Implementation Approach
- Create a new branch for the Java 17 upgrade
- Apply changes to build files, CI workflow, and documentation
- Replace or refactor deprecated API usage
- Run all tests and confirm parity with Java 8 outputs
- Open PR with the changes, migration notes, and CI results
You only need to look in the following repo: BankOfDevin/BankingServer.
Tier-1 Bank: 11x Faster Java 8 → 17 Migration
- Context:
A leading North American bank needed to upgrade Java 8 applications to Java 17 to strengthen security and maintain regulatory compliance.
- Challenge:
Migrate dozens of Spring Boot–based services from Java 8 while addressing deprecated APIs and outdated dependencies.
- Solution:
Devin automated build updates, dependency migrations, and CI/CD modernization.
- Outcome:
The migration finished in weeks, with tests confirming identical behavior across all services.
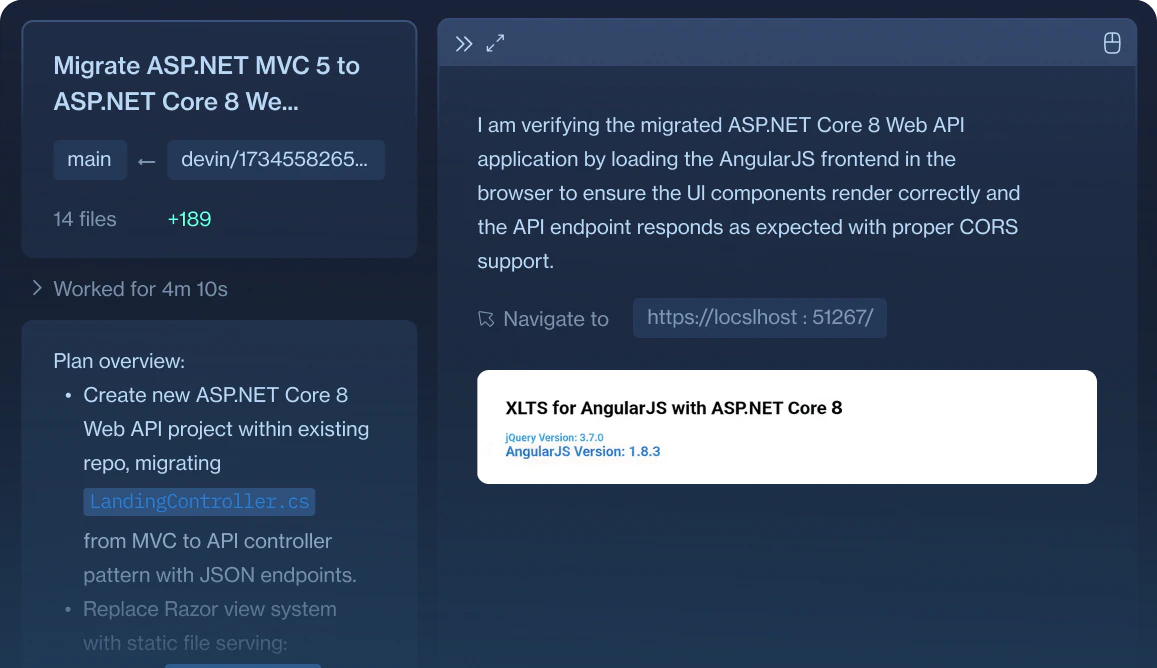
.NET Upgrades
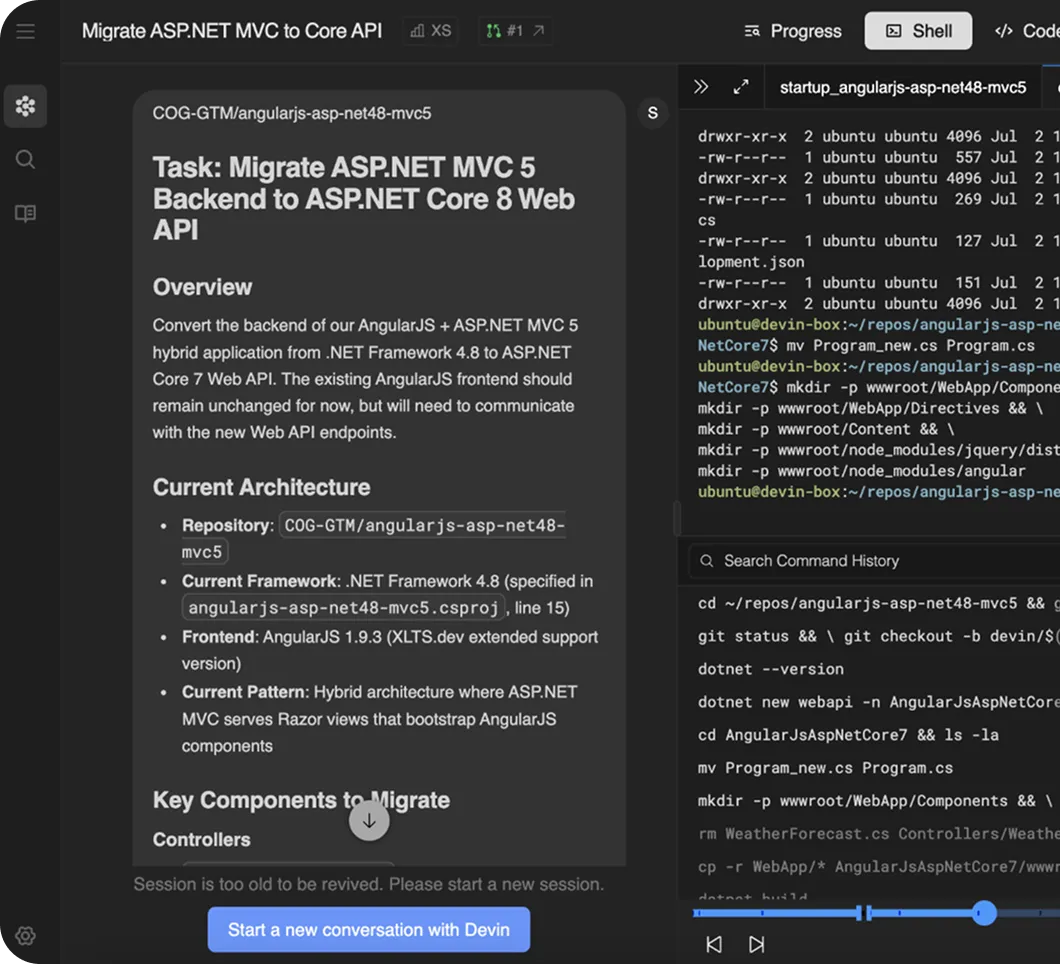
Devin automates migrations from ASP.NET Core 3 → 7 to .NET 8, using your private NuGet store to update dependencies, and ensure sample libraries such as json serialization work properly.

Devin’s Workflow<br/>ASP.NET MVC 5 to ASP.NET Core 8
- Analyze & plan Identify controllers, routes, configs, and dependencies.
- Scaffold project Create ASP.NET Core 8 Web API with SDK setup.
- Migrate logic Convert controllers and replace web.config with middleware.
- Test parity Run tests to confirm identical outputs.
- Open PR Open pull request with code and migration notes.

Devin Prompt
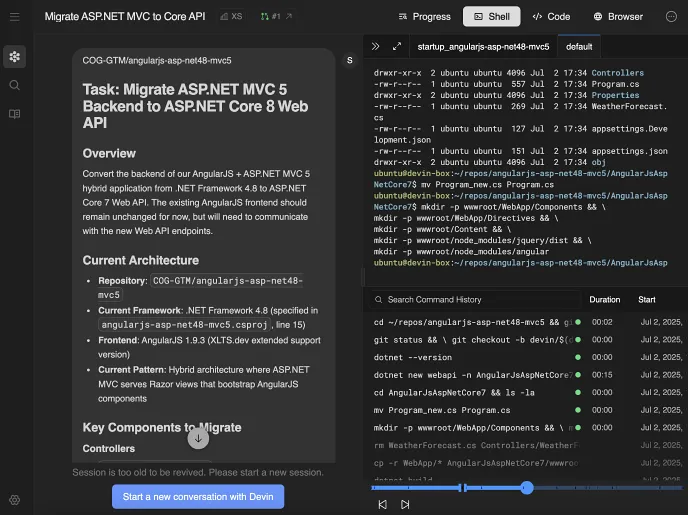
Hey Devin,
Please migrate the ASP.NET MVC 5 backend from the COG-GTM/angularjs-asp-net48-mvc5 repository to an ASP.NET Core 8 Web API project. Here’s your task breakdown:
Create a new ASP.NET Core 8 Web API project
- Set up the project structure following ASP.NET Core conventions.
- Add
Program.csandStartup.csfor configuration.
Migrate controllers
- Convert all MVC controllers (e.g.,
LandingController.cs) into API controllers. - Ensure all endpoints return JSON responses with appropriate status codes.
- Keep the same route patterns to avoid frontend changes.
Handle configuration files
- Replace
App_Start/BundleConfig.csandApp_Start/RouteConfig.cswith ASP.NET Core equivalents.
Update views and static files
- Remove Razor views (e.g.,
Views/Landing/Index.cshtml). - Serve the AngularJS app (HTML, JS, CSS) as static files from the
wwwrootfolder.
Enable CORS
- Add middleware to allow requests from the current AngularJS frontend at
http://localhost:51267/.
Set up dependency injection
- Register services in
Program.csusing the DI container.
Match frontend expectations
- Preserve AngularJS app structure (
WebApp/app.js,WebApp/Components/test.component.js, etc.). - Maintain route compatibility so the frontend doesn’t break.
- The AngularJS app is initialized as
angular.module('app', []); this should remain unchanged.
Deliverables
- New ASP.NET Core 8 Web API project with migrated controllers.
- Static file serving configuration for the AngularJS frontend.
- CORS configuration to enable frontend requests.
- Documentation of any route changes or adjustments.
References
- The original project structure is defined in
angularjs-asp-net48-mvc5.csproj, and AngularJS dependencies are inpackage.json. - You only need to look in the following repo:
COG-GTM/angularjs-asp-net48-mvc5.
Digital Bank: 120 Repos Upgraded to .NET 8 in 2 Weeks
- Context:
A leading digital bank needed to modernize hundreds of .NET repositories to improve performance and reduce maintenance costs.
- Challenge:
Upgrade 120 repositories from .NET 3 to .NET 8, originally scoped for two years with five engineers.
- Solution:
Devin automated the upgrades, generating modern projects and parity tests.
- Outcome:
The migration finished in two weeks with one engineer.
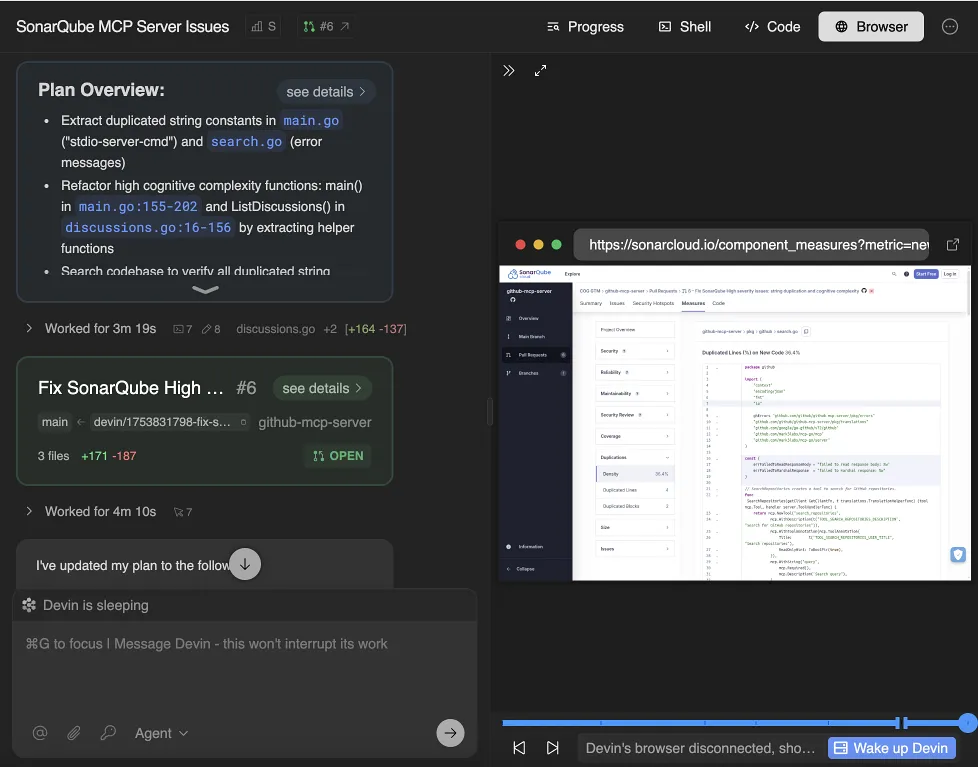
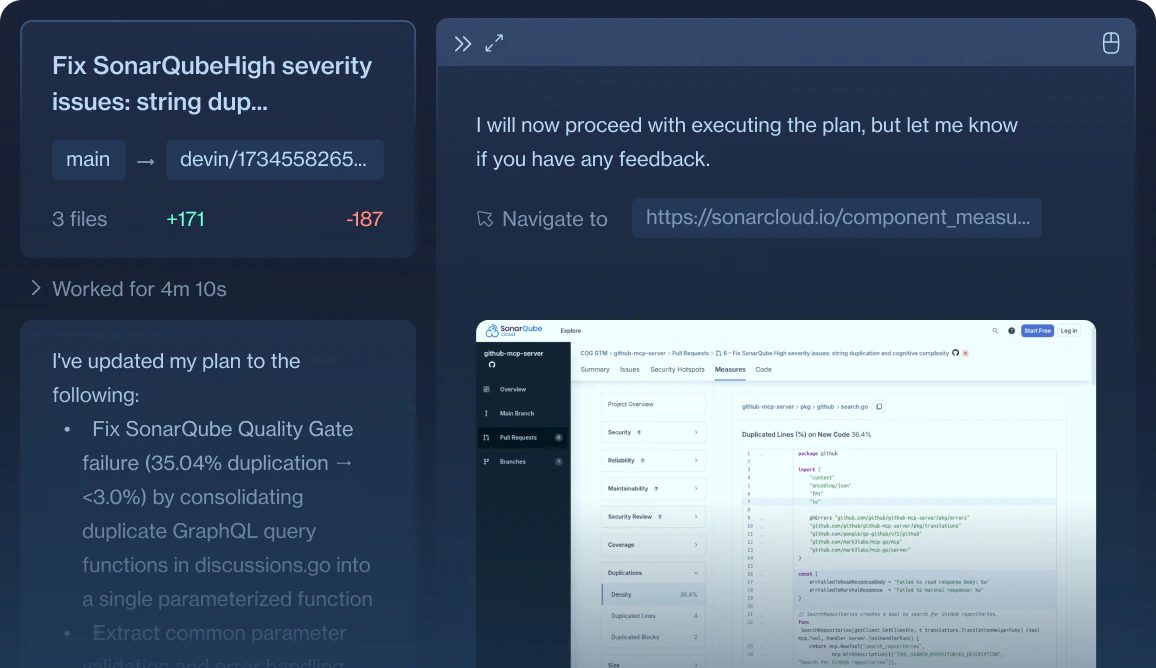
Security Remediation
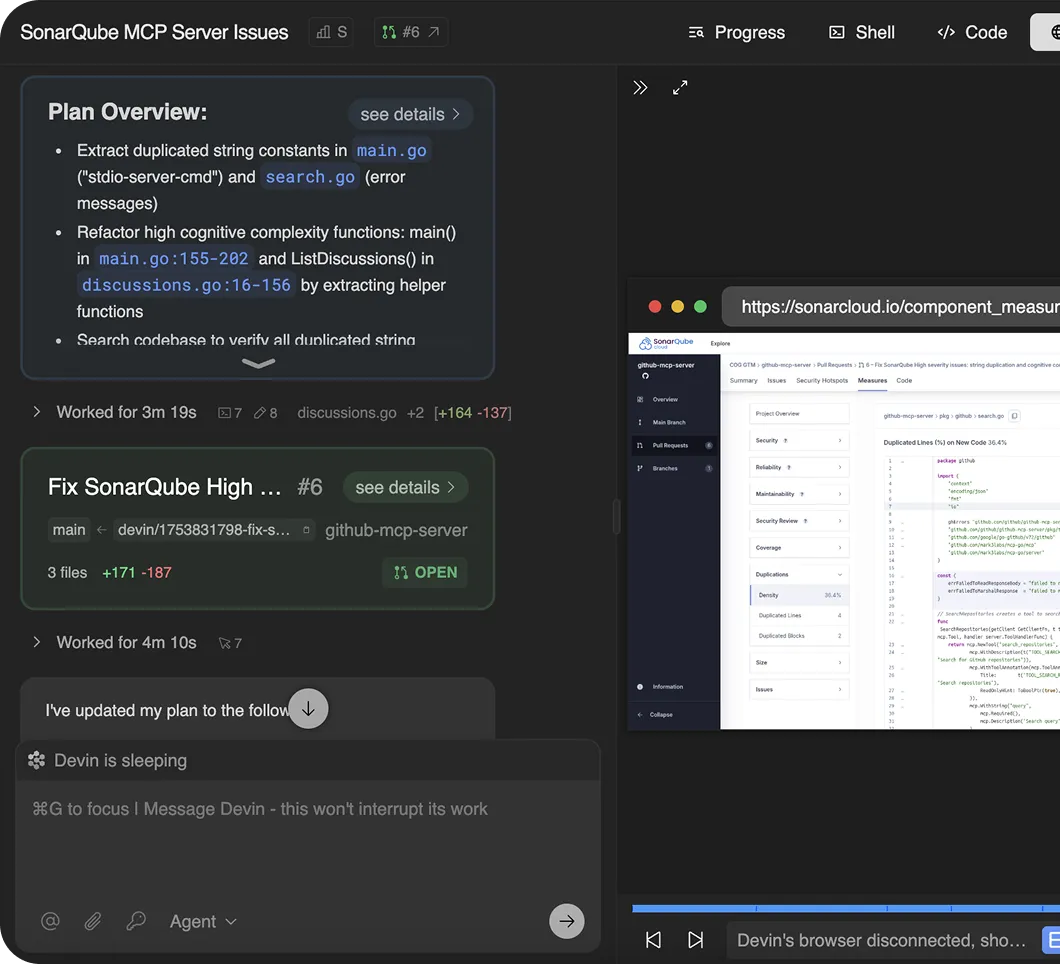
Devin connects to SAST tools via API, and is able to automatically remediate code-smells, create a pull request, and validate its work automatically using CI/CD feedback.

Devin’s Workflow<br/>SonarQube → Fix + PR
- Analyze Pull high-severity findings from SonarQube (e.g., vulnerabilities, duplication, complexity).
- Plan Propose refactoring steps with confidence rating.
- Fix Fix vulnerabilities, consolidate duplicates, simplify complex functions.
- Validate Run lint/tests and confirm CI/CD validation and Quality Gate passes.
- PR Open pull request with code changes and linked issues.

Devin Prompt
Hey Devin,
Please connect to the SonarQube API server for the BankOfDevin/BankingServer repository.
Identify and extract issues for the following critical vulnerability SonarQube tags:
- SQL Injection
- XSS attacks
Implement targeted fixes
- Resolve 2 issues from the SQL Injection category.
- Resolve 2 issues from the XSS category.
Validate remediation
- Run regression tests and lint checks.
- Ensure all fixes pass SonarQube’s Quality Gate for high-severity issues.
Deliverable
- Open a pull request with the fixes.
- Include SonarQube issue links and test results in the PR description.
- Use ticket ID SonarQube-42 in the PR description.
You only need to look in the following repo: BankOfDevin/BankingServer.
Let me know if you need any clarification on the requirements.
Tier-1 Bank: 700+ Vulnerabilities Remediated at 20x Speed
- Context:
A major North American bank needed to clear a backlog of high-severity vulnerabilities flagged by static analysis tools.
- Challenge:
Fix critical security issues (e.g., insecure dependencies, hardcoded secrets, complex functions) at scale without slowing feature delivery.
- Solution:
Devin integrated with the security toolchain, ran scans, and applied targeted fixes.
- Outcome:
Devin remediated 700+ vulnerabilities during the pilot period alone.
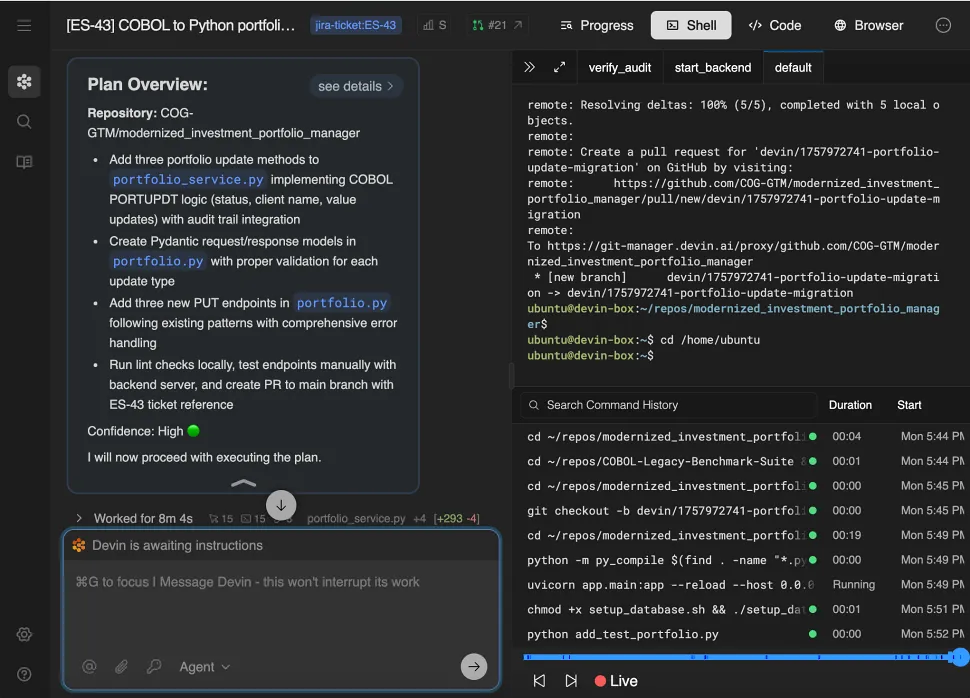
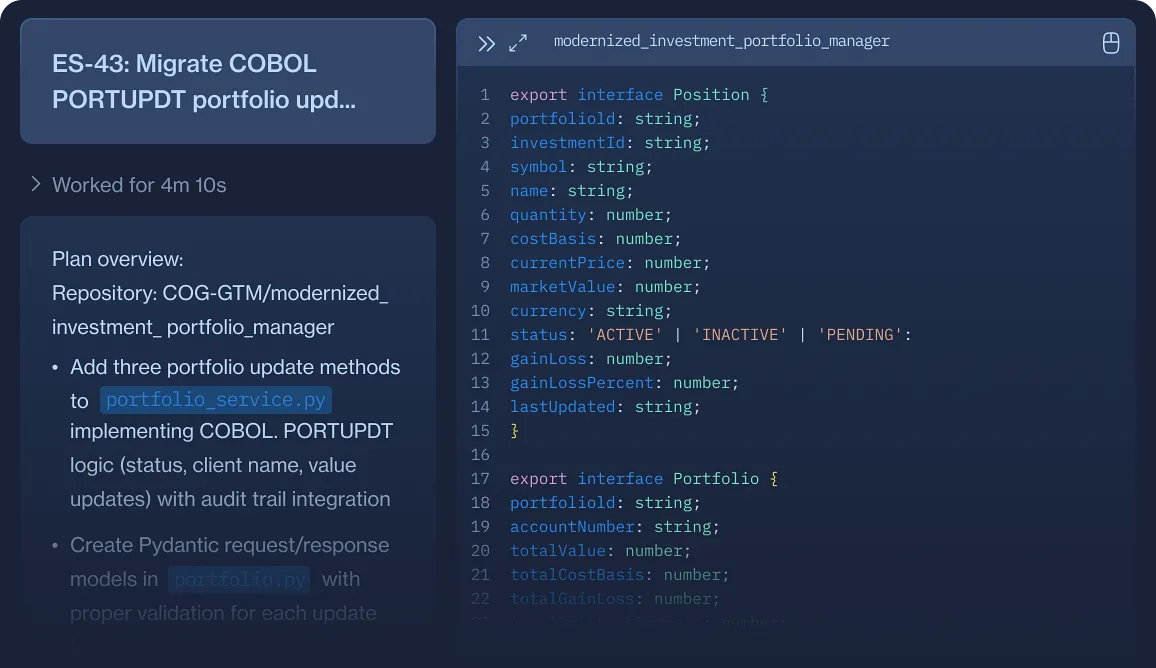
Mainframe / COBOL Migrations
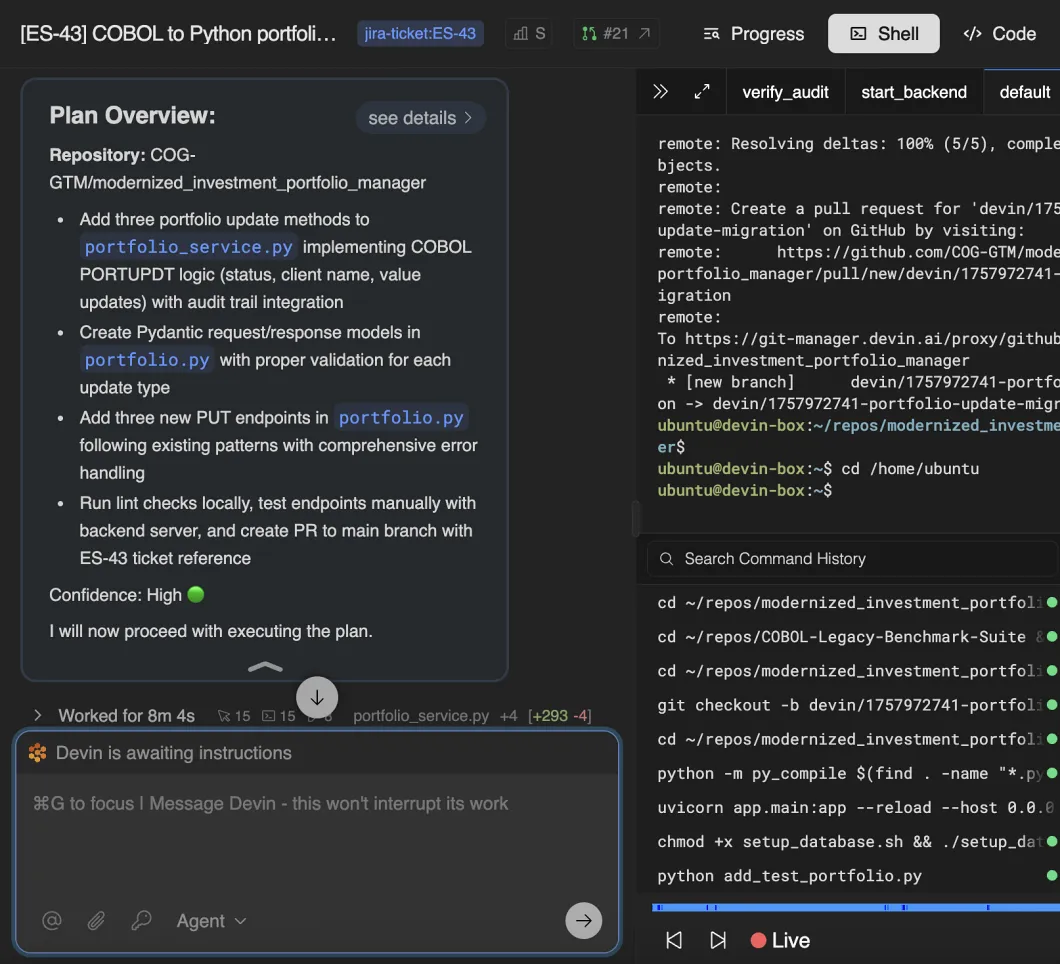
Devin automates the migration of COBOL programs into modern languages and environments, with regression tests to confirm identical behavior.

Devin’s Workflow<br/>COBOL → Java
- Analyze & plan Identify COBOL programs, record layouts, and file rules.
- Structure migration Convert COBOL snippets into equivalent Java structures.
- Migrate logic Translate COBOL logic into Java classes and methods.
- Test parity Run golden-file tests to confirm identical outputs.
- Open PR Open pull request with test results and ticket ID for review.

Devin Prompt
Hey Devin,
Please create a Java implementation of the COBOL control file for investment account balances from the Devin-Bank/Cobol-Investment-App repository. Here’s your task breakdown:
Create these core Java classes
-
AccountBalanceRecord— Java POJO mirroring the COBOL record layout (use exact field sizes/types from the PIC clauses in the source):accountId(e.g., 10 chars)asOfDate(e.g., 8 chars, YYYYMMDD)currency(3 chars)txnType(1 char; e.g., D/C)amount(signed, 2-decimal fixed width; support COMP-3 if present)runningBalance(signed, 2-decimal fixed width)
-
FixedWidthFileReader/FixedWidthFileWriter— Utilities that reproduce COBOL fixed-width I/O semantics:- Space/right padding, truncation rules, and collating sequence
- Packed/zoned decimal (COMP-3/COMP) parsing if used; otherwise DISPLAY numeric
- File status mapping (e.g., 00, 10, 23) to Java exceptions with recoverable handling
-
BalanceControlProcessor— Implements the COBOL “control” logic:- Open/read sequential input(s), perform control-break processing on
accountId(andasOfDateif the COBOL does so) - Apply debits/credits to compute running balances exactly as in COBOL
- Emit headers/trailers and control totals (record counts, sum of debits/credits, final balances)
- Open/read sequential input(s), perform control-break processing on
Implement the program workflow
- Use the same file names as the COBOL program (inputs, outputs, and any work files).
- Example (adjust to match the source):
- Inputs:
INVESTMENT-TXN.DAT,ACCT-MASTER.DAT - Outputs:
BALANCE-REPORT.TXT,CONTROL-SUMMARY.TXT,ERROR-LOG.TXT - Maintain fixed-width record format end-to-end (identical field widths and alignment).
- Replicate control breaks and totals exactly: emit group totals when keys change; reproduce header/trailer lines byte-for-byte where feasible.
- Numeric rules: match COBOL rounding/truncation and sign handling (assume scale 2; implement half-up unless the PIC/usage dictates otherwise).
- Error handling: on malformed records, log to
ERROR-LOG.TXTwith record image + reason, then continue. - Deterministic results: for identical inputs, outputs must match COBOL outputs.
Match COBOL’s file handling
- Use identical file names/paths expected by the control file.
- Respect open modes, end-of-file semantics (AT END), and status codes.
- Preserve any sort/merge steps if present (use in-memory stable sort keyed exactly as in COBOL).
Implement verification
- Create golden-file tests that run the Java flow against sample inputs from the repo (or ones you generate to mirror the COBOL examples) and byte-compare outputs to the COBOL program’s results.
-
Include unit tests for:
- PIC/usage → Java parsing (including COMP-3 if applicable)
- Control-break emission
- Totals/rounding parity
Repository scope
- You only need to look in the following repo:
Devin-Bank/Cobol-Investment-App. - The original COBOL control file is located in the
investment_balancedirectory (use it as the source of truth for record definitions, file names, and control logic).
Deliverables
-
Production-quality Java source with README explaining:
- Field mappings (PIC → Java), rounding/sign rules, and any assumptions
- How to run the job and the tests
- A PR with the description including ticket ID MBA-18 and a brief summary of parity test results.
Let me know if you need any clarification on the requirements.
Tier-1 Bank: Millions of COBOL records modernized
- Context:
One of the largest financial institutions in Latin America, serving 60M+ customers, needed to modernize legacy COBOL systems to meet new regulatory requirements.
- Challenge:
Migrate national tax identifier fields (CNPJ) from 10-digit numeric to 14-digit alphanumeric across thousands of COBOL modules.
- Solution:
Devin automatically migrated thousands of files with high accuracy.
- Outcome:
COBOL team is now ahead of schedule on the CNPJ migration.
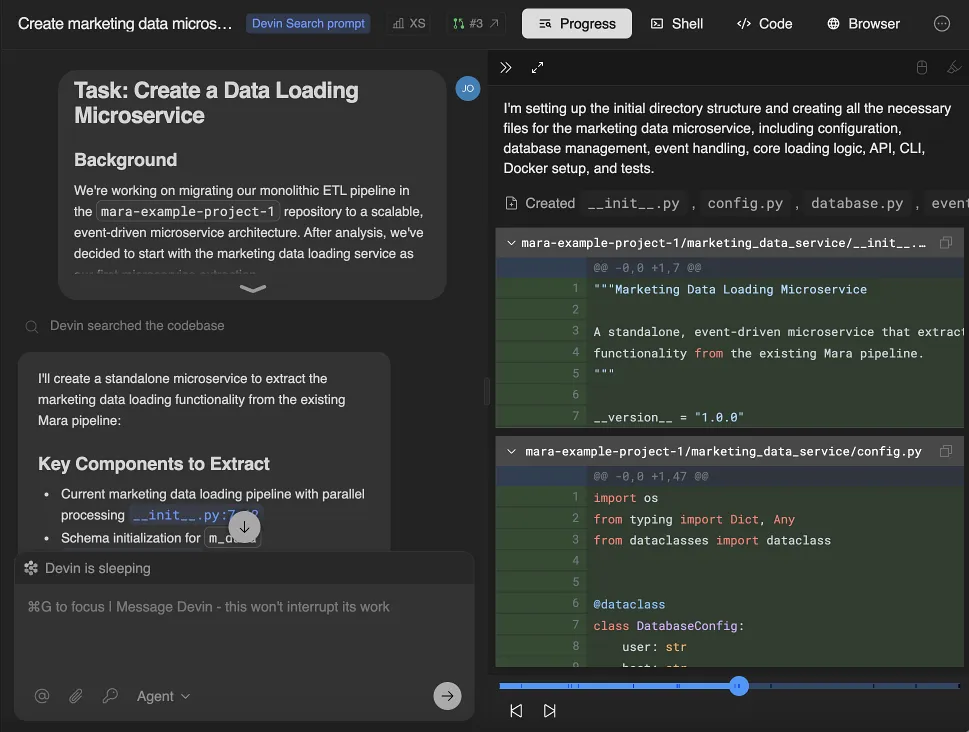
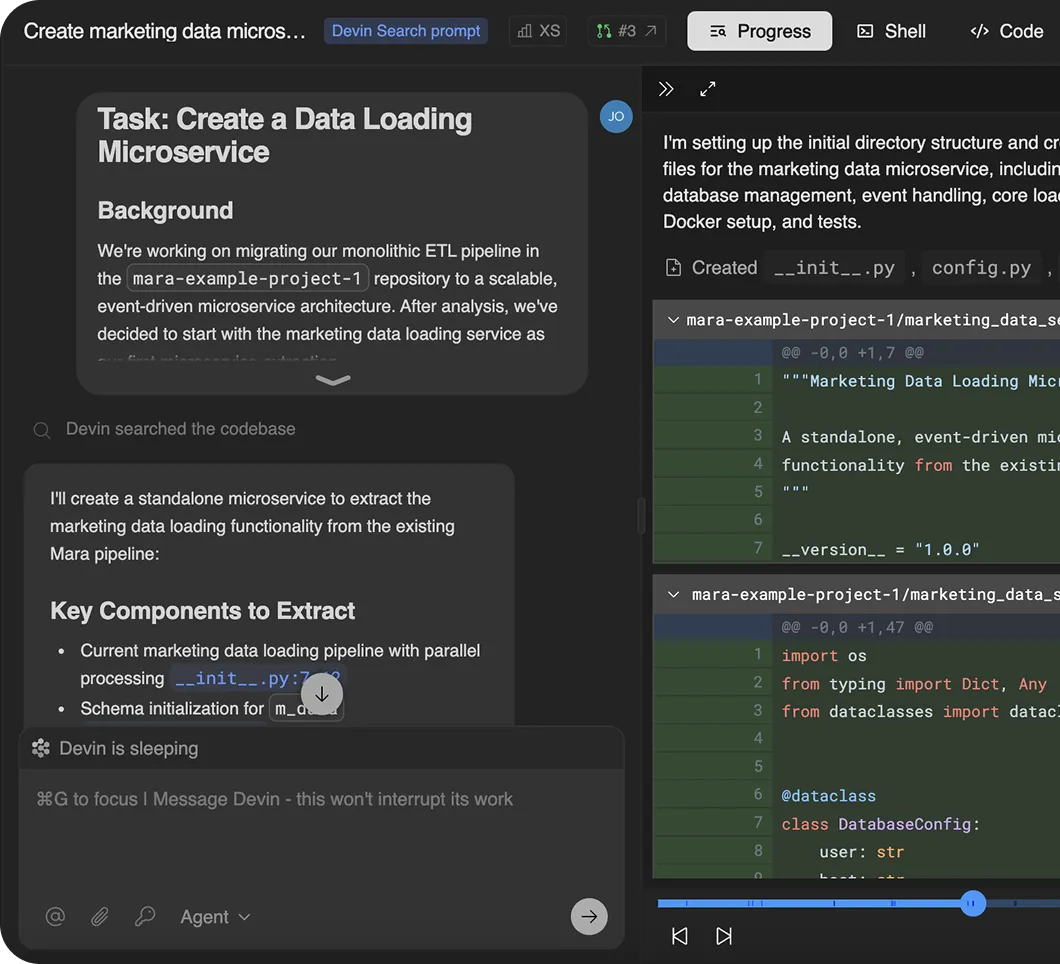
Legacy ETL Migrations
Devin automates the migration of ETL jobs into event-driven microservices, generating service scaffolds, CI/CD pipelines, and regression tests to confirm outputs remain identical.

Devin’s Workflow<br/>Legacy ETL → Event-Driven Microservices
- Analyze & plan Identify ETL jobs, mappings, and transformations.
- Scaffold service Generate microservices with CI/CD and monitoring.
- Migrate logic Rewrite legacy ETL into event-driven functions (Kafka, Pub/Sub).
- Test parity Run regression tests to confirm identical outputs.
- Open PR Create pull request with code, tests, and migration notes.

Devin Prompt
Hey Devin,
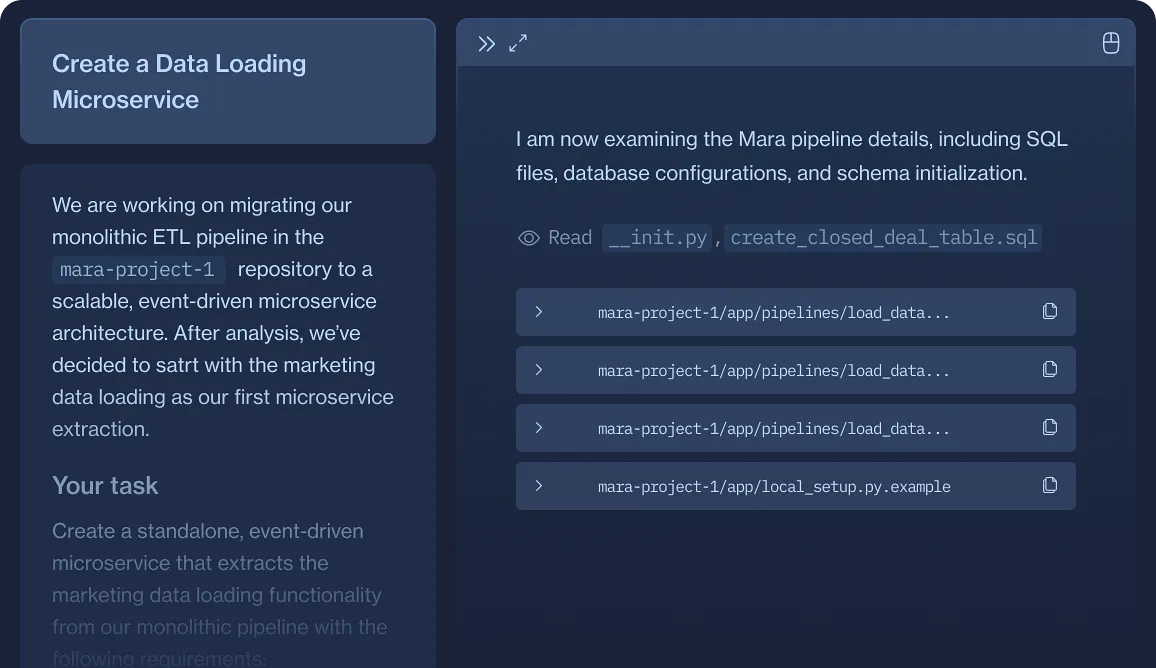
Please create a standalone, event-driven microservice that extracts the load_transaction_data pipeline from the Devin-Bank/ETL repository. Here’s your task breakdown:
Core Functionality
- Monitor and extract data from
banking.transactionsandbanking.customer_accountstables in the olist source database. - Load this data into
b_data.transactionsandb_data.customer_accounttables in our data warehouse. - Support concurrent loading of both tables (parallel processing).
Event-Driven Architecture
- Implement listeners for database change events (new transactions, account updates) or scheduled triggers.
- Publish
transaction-data-loadedevents when loads complete successfully. - Publish failure events with retry capabilities when errors occur.
Technical Requirements
- Create connection management for both olist (source) and dwh (target) databases.
- Implement schema initialization for the
b_dataschema before loading data. - Add data validation to ensure transaction and account integrity during the copy process.
- Implement monitoring for load times, record counts, and failures.
Migration Considerations
- Maintain backward compatibility so the service can still be called by the existing ETL pipeline during transition.
- Implement idempotency to allow safe re-runs without duplication.
- Provide a rollback strategy to revert failed loads.
The new microservice should preserve the same data flow and transformation logic as the current ETL, but replace the monolithic pipeline structure with an event-driven architecture.
Deliverable
- Create a PR with your implementation and include the ticket ID ETL-42 in the PR description.
The original load_transaction_data pipeline is in the Devin-Bank/ETL repo. Use this as your reference for exact functionality matching.
<span>Nubank: 65,000 Files Migrated, 8.2x Efficiency Gain</span><div class="o-icon"> <svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="30" height="16" viewBox="0 0 30 16" fill="none"> <g clip-path="url(#clip0_5019_2792)"> <path d="M19.4443 4.78516C19.4443 6.81902 19.4544 8.57511 19.4775 9.2832C19.5792 12.3659 21.404 14.3033 24.2227 14.3057C25.0731 13.4071 25.5294 12.3087 25.5967 10.6289C25.6059 10.3946 25.6037 9.56412 25.6006 8.46973C25.599 7.90264 25.5971 7.26423 25.5967 6.60156C25.5939 3.72283 25.5967 0.375572 25.5967 0.362305H29.3828V7.17285C29.3828 7.40622 29.3873 7.64165 29.3916 7.87793C29.4002 8.35314 29.4086 8.83241 29.3828 9.30664C29.34 10.097 29.2037 10.8739 28.835 11.5957C27.9905 13.2497 26.2596 14.3154 24.415 14.3154C24.3507 14.3154 24.2863 14.3142 24.2227 14.3115C23.3157 15.2642 22.1125 15.8203 20.6992 15.8203C17.9458 15.8203 16.1202 13.8104 15.7715 10.7988C15.6582 9.82071 15.659 8.44091 15.6602 6.84375V0.363281L19.4443 0.359375V4.78516ZM9.41602 -0.00195312C12.1695 -0.00190434 13.9955 2.00877 14.3447 5.02051C14.458 5.99856 14.4562 7.37755 14.4551 8.97461V15.4561H10.6689V11.0303C10.6689 11.0015 10.6607 7.24047 10.6377 6.53516C10.5361 3.45221 8.71057 1.51478 5.8916 1.5127C5.04114 2.41125 4.58576 3.5106 4.51855 5.19043C4.50934 5.42532 4.51159 6.25571 4.51465 7.34961C4.51624 7.91654 4.51807 8.55434 4.51855 9.2168C4.52134 12.0831 4.51859 15.4141 4.51855 15.4561H0.731445V8.64551C0.731441 8.41226 0.7279 8.17659 0.723633 7.94043C0.715049 7.4654 0.705708 6.98669 0.731445 6.5127C0.774227 5.72213 0.911386 4.94463 1.28027 4.22266C2.12464 2.56875 3.85479 1.50407 5.69922 1.50391C5.76365 1.50391 5.82878 1.50511 5.89258 1.50781C6.79958 0.554948 8.00259 -0.00195312 9.41602 -0.00195312Z" fill="#F2F5FA"/> </g> <defs> <clipPath id="clip0_5019_2792"> <rect width="30" height="16" fill="white"/> </clipPath> </defs> </svg> </div>
- Context:
Nubank needed to modernize thousands of legacy ETL jobs spanning 500k+ lines of code, which had become costly to run and hard to scale.
- Challenge:
Nubank had an ETL migration scoped over 6 months with 50 engineers.
- Solution:
Devin automated the extraction of ETL logic, generated microservices, and validated outputs with regression tests.
- Outcome:
With Devin, Nubank achieved the migration in 1/3rd the time for less than 1/10th the cost.
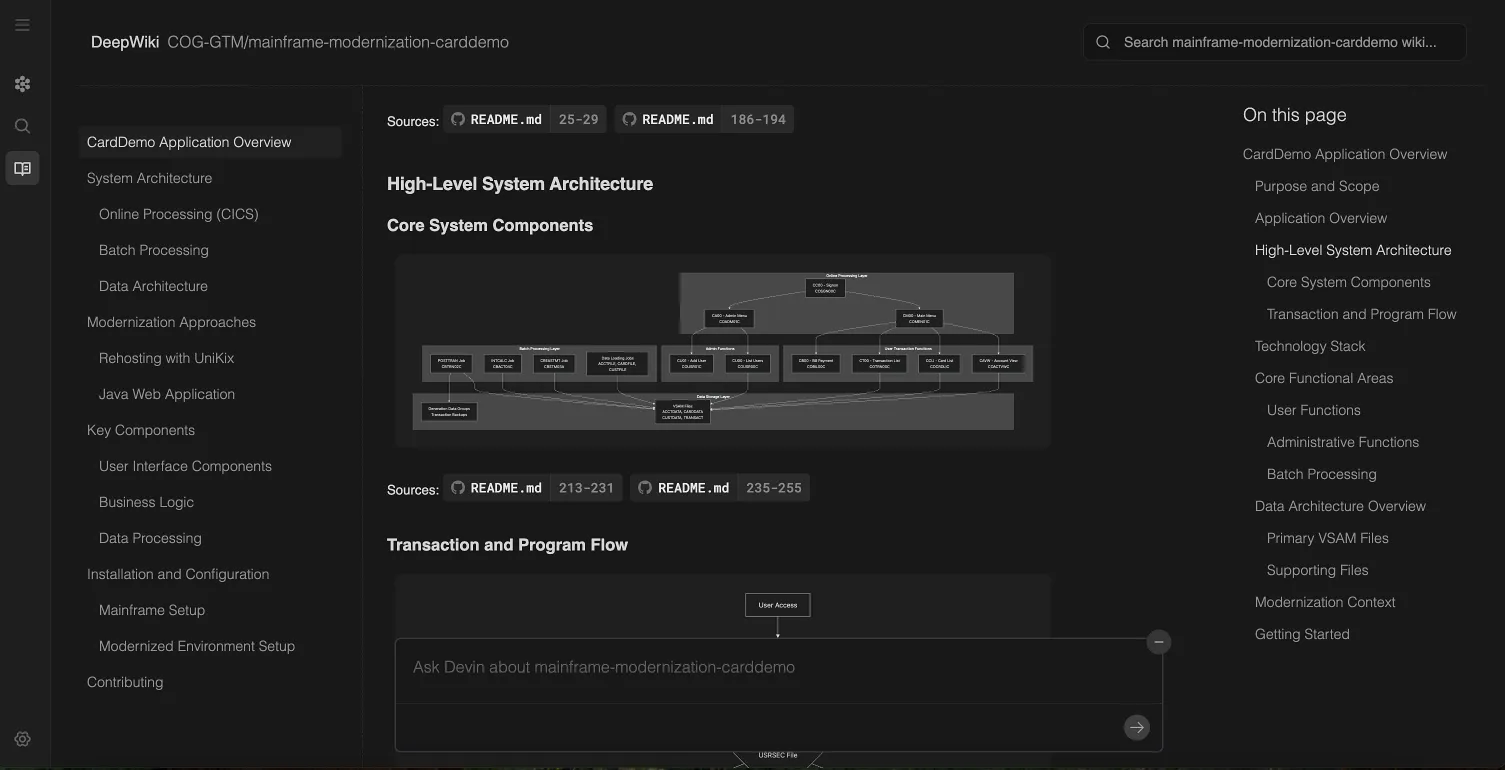
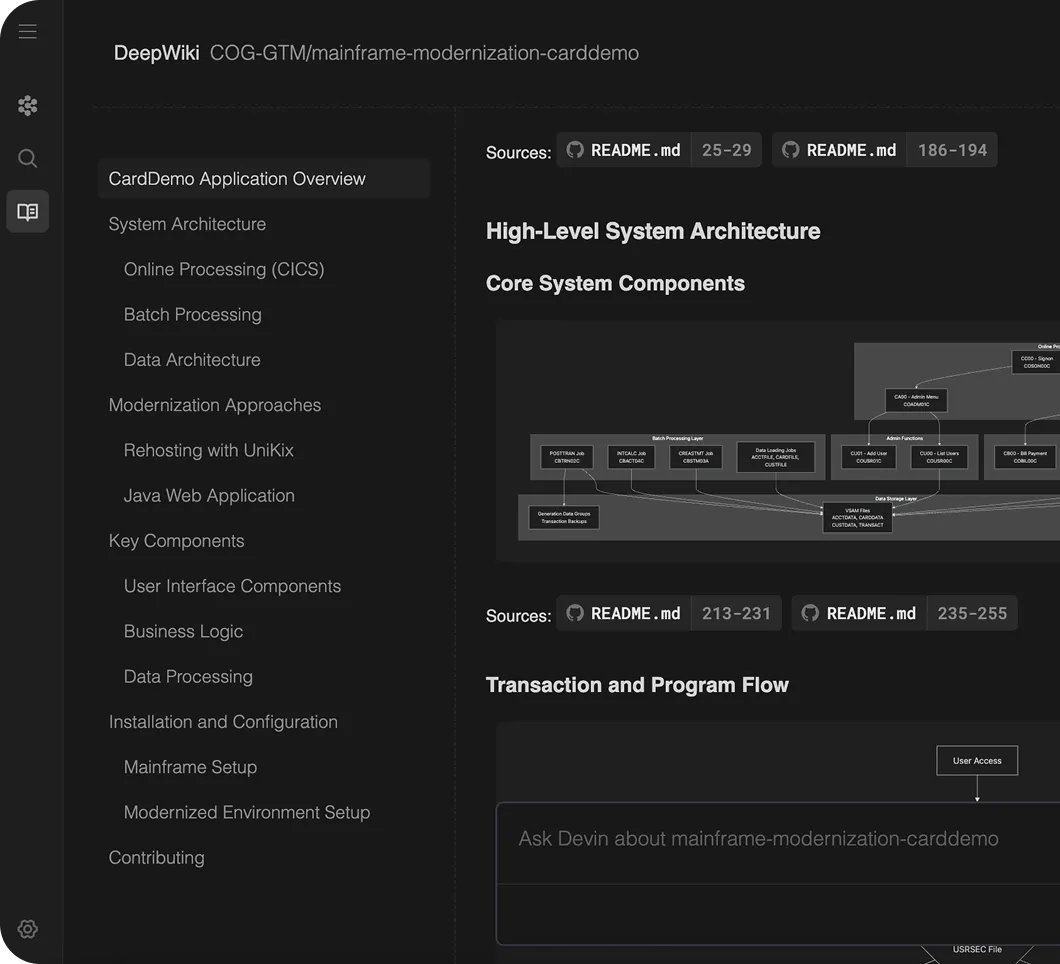
Custom & Proprietary Systems
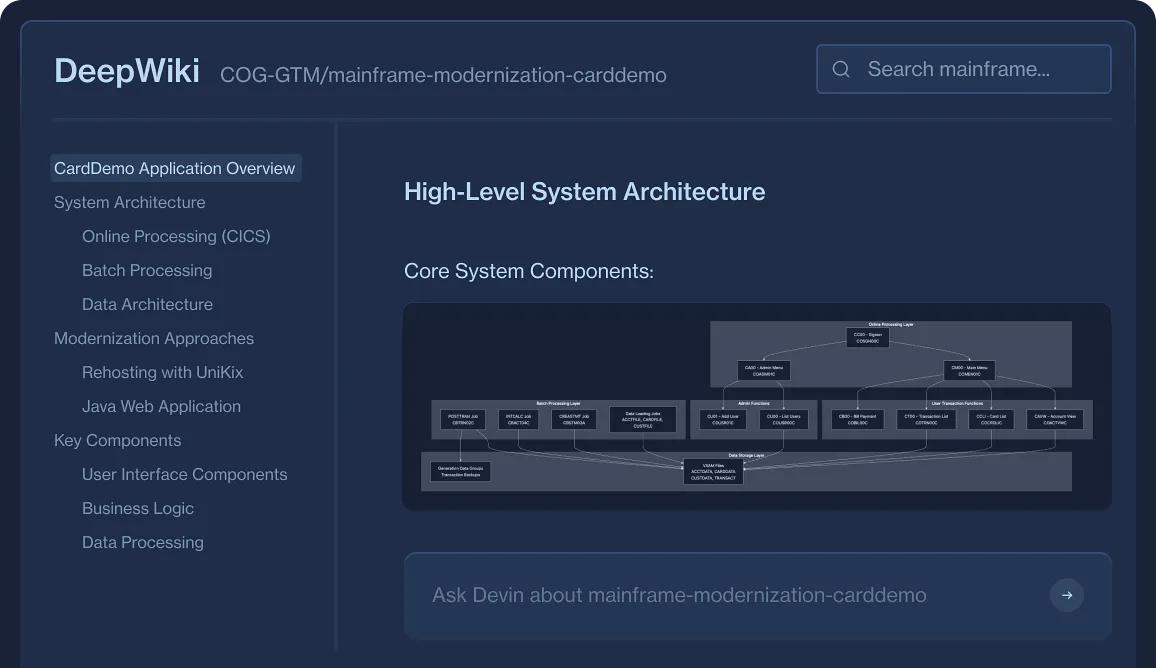
Devin succeeds because it’s an agent, not a static model: it can learn proprietary systems, generate modern replacements, and validate outputs with tests.

Devin’s Workflow<br/>Proprietary Protocol → Modern Service
- Learn Learn proprietary languages and frameworks via DeepWiki indexing.
- Plan Select components to migrate into modern services.
- Migrate Re-implement logic in standard languages.
- Test Validate via CI/CD against historical outputs.
- PR Open PR with tests and migration notes.

Devin: Agent Advantage
- Model vs. Agent Traditional tools are trained for known languages; Devin acts as an agent that can explore, reason, and adapt.
- Any language, any framework From C++ to COBOL variants to proprietary DSLs — Devin is not constrained by pretraining.
- Output guarantees Golden-file tests, regression checks, and CI/CD pipelines ensure the migrated system behaves identically.